Flow chemistry smart plant
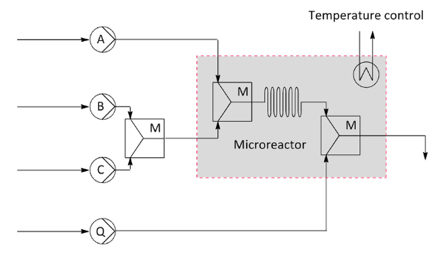
In a continuous flow system, a chemical reaction is carried out with a continuous supply of substrate and reagents. The basic principle of a continuous flow system is shown schematically in the figure below. In this commonly used setup, two flows (denoted as Flow A and Flow B) are pumped into a micro reactor. Future Chemistry’s micro reactors are small continuous flow reactors made from glass, combining excellent mixing and channels for reaction with excellent temperature control. After being mixed, the solutions will start reacting. When the combined flow reaches the end of the micro reactor, a third flow is introduced to stop the reaction. This is called the quenching flow, and is denoted as Flow Q
While automation and controls have existed for decades, the fully smart plant has only recently gained traction as a viable pursuit for manufacturers. Five overarching trends seem to be accelerating the drive toward smart plant
- Rapidly evolving technological capabilities
- Increased supply chain complexity and global fragmentation of production and demand
- Growing competitive pressures from unexpected sources
- Organizational realignments resulting from the marriage of IT and OT
Flow chemistry differs from conventional batch chemistry by having the following important features
- Flow of reagents
- Control of reaction time
- Control of stoichiometry
- Heat transfer
- Mass transferr
- Flow chemistry is easily scaled
- Precise control
- Low inventory of materials
- Telescoped reactions
- No head-spacel
- Very low back-mixing
The implementation of continuous flow processing as a key enabling technology has transformed the way we conduct chemistry and has expanded our synthetic capabilities
Cotrydo convert batch to continuous process and develop the entire process steps under the principle of flow chemistry with process intensification.
| Process | sample digitization opportunities |
|---|---|
| Manufacturing operations |
|
| Warehouse Operations |
|
| Inventory tracking |
|
| Quality |
|
| Maintenance |
|
| Environmental,health and safety |
|
Benefits
Undertaking a smart factory journey generally addresses such broad categories as asset efficiency, quality, costs, safety, and sustainability. These categories, among others, may yield benefits that ultimately result in increased speed to market; improved ability to capture market share; and better profitability, product quality, and labor force stability.
Cotrydo offers the smart way of converting any plant in to smart plant by using the above methodology



